2017
Certification for compliance with the ISO 9001:2008 quality management standard. The certificate relates to "Scientific work on the effects of nuclear and electromagnetic radiation as well as the implementation and development of methods for their characterization".
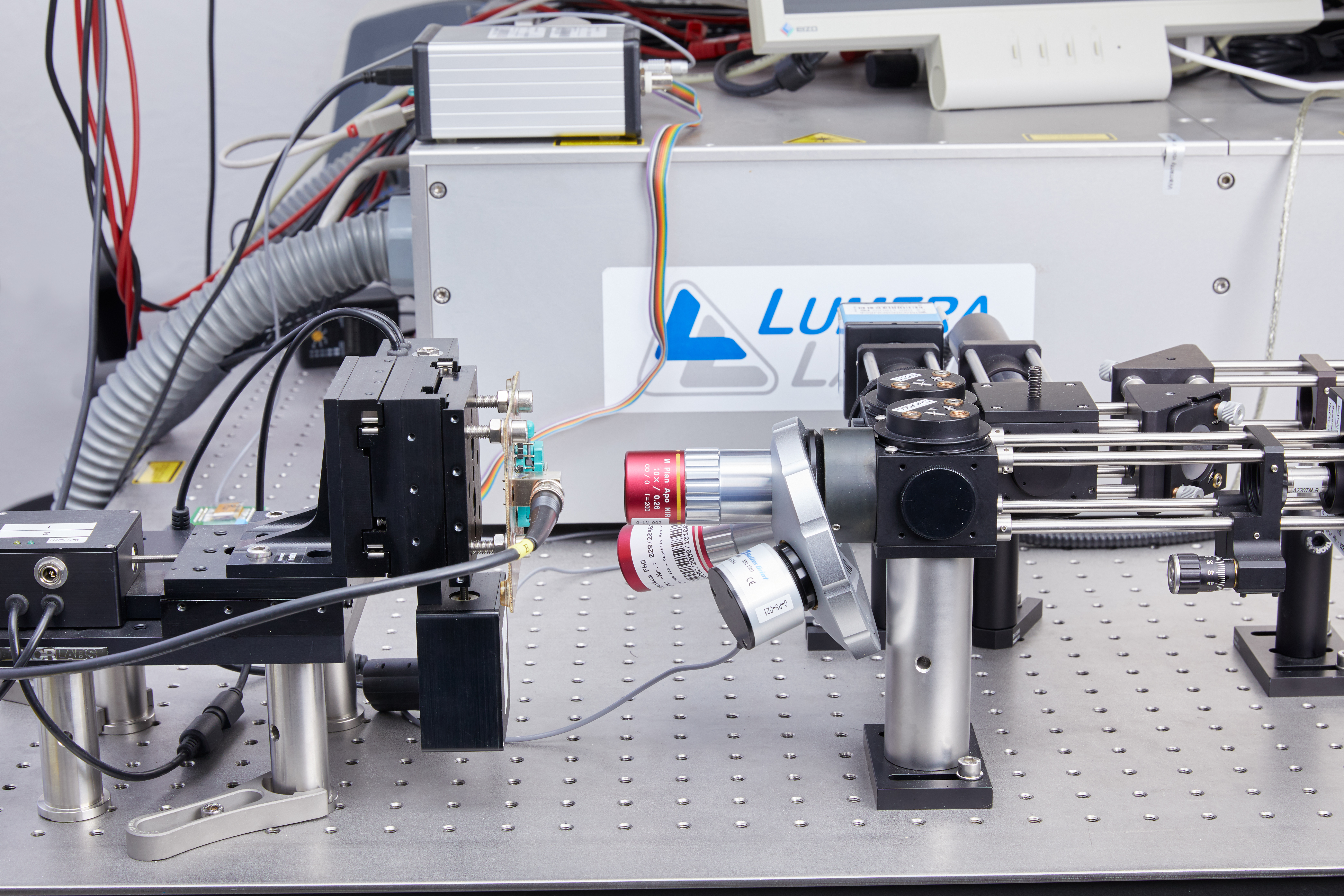
In addition, the first series of tests with the picosecond laser for mapping single event effects are launched.
Receipt of a grant of 1.2 million euros from the Federal Office of Bundeswehr Equipment, Information Technology and In-Service Support for the KATI assistance system.
This year also sees the founding of the "Fraunhofer Group for Innovation Research" to strengthen its role in the research, technology and innovation policy dialog with industry, politics and society. Fraunhofer INT is one of four founding members.
2018
The Institute organizes the "F&T-Zukunftslagekonferenz" for the first time on behalf of and chaired by the Director of Research at the Federal Ministry of Defence with 70 participants. The conference has been held annually since then, with the exception of the years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
2019
Start of construction work to extend the experimental hall. The largest part of the extension is taken up by a new anechoic chamber, in which 170 m³ are available for investigations in the field of electromagnetic compatibility.
2021
Fraunhofer INT and Digital Science combine Technology Foresight Tool KATI and Dimensions data, making the KATI-system commercially usable outside Fraunhofer INT.
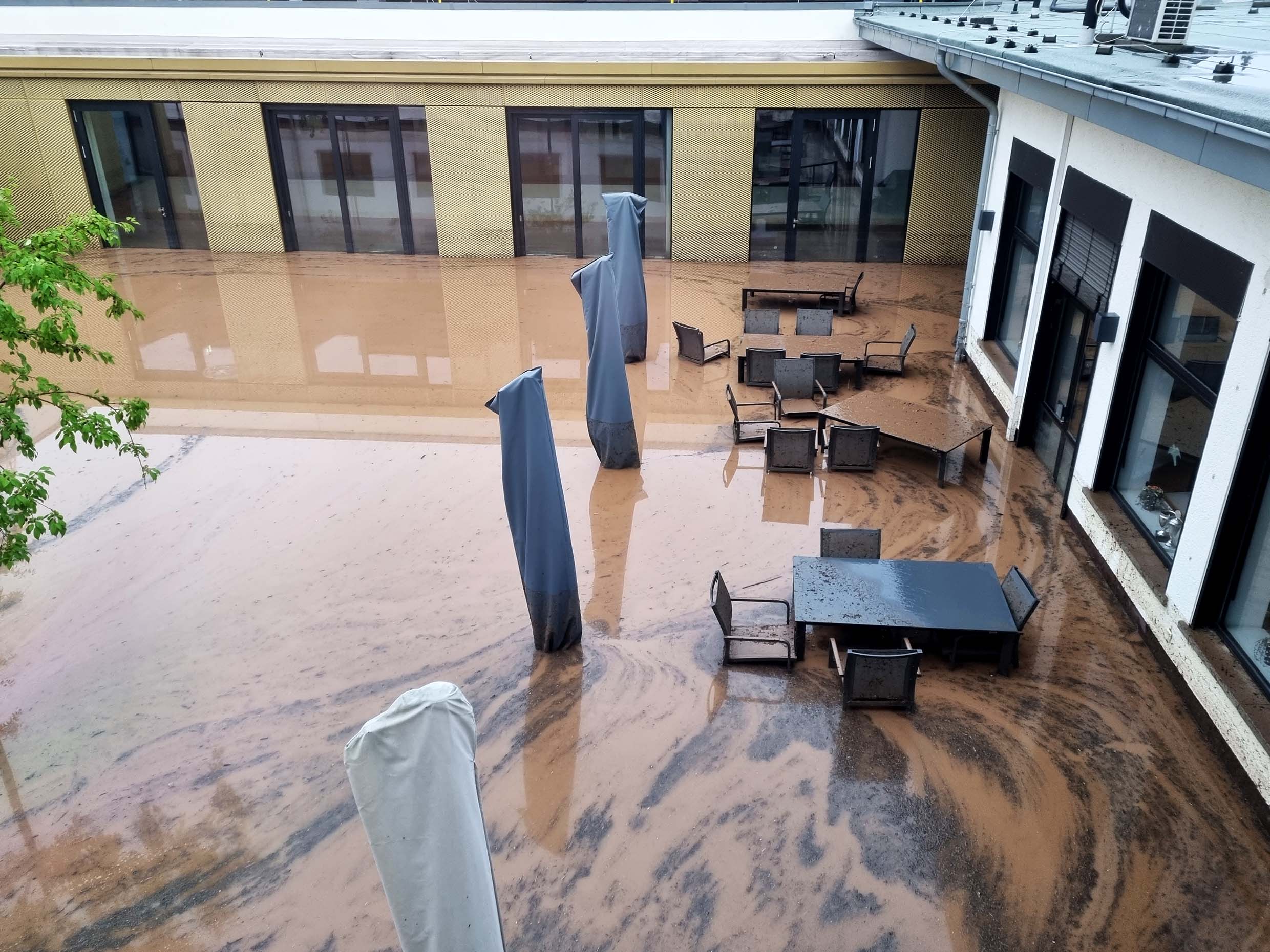
On the night of July 14-15, a tidal wave floods Euskirchen. The entire Institute site is flooded. At times, the buildings are up to 86 cm under water and the basement area is completely flooded.
2022
Fraunhofer Space Alliance becomes Fraunhofer AVIATION & SPACE. The SPACE office remains at Fraunhofer INT.
The second book "Neue Technologien - Kernthemen des Technologiemonitorings am Fraunhofer INT zwischen 2009 und 2021" is published.
2023
The Onboard Radiation Sensor (FORS) developed at Fraunhofer INT will start its mission in space on the Heinrich Hertz satellite on July 5, 2023.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Technological Trend Analysis INT
Fraunhofer Institute for Technological Trend Analysis INT